
Pedigree analysis suggested an X-linked, recessive hereditary pattern in one pedigree and autosomal recessive inheritances in the other three pedigrees. DiscussionĪ study, reported that patients with characteristics of non-syndromic hereditary auditory neuropathy were identified in one large and three smaller Chinese families. Hearing aid trail was conducted for both father and daughter with high gain, super power hearing aids (Oticon Dynamo SP 4) and was not found to be beneficial in speech understanding. Below Figures 1,2 are the ABR waveforms of the individuals where ringing cochlear mechanics can be observed in the initial time window and absence of peak V in later time window suggesting a neural pathology.įigure 1,2: Waveforms of auditory brainstem response of Case 1 and Case 2 showing presence of cochlear microphonics and absence of ABR. Cochlear microphonics was seen up to 2 ms in both individuals indicating normal functioning of the cochlear mechanics. Wave polarity was reversed to check for the ringing cochlear microphonics, the presence of which indicates a normal cochlear functioning. No clear and replicable peak V was observed in both ears at 90dBnHL for both the individuals. Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) was done to assess the performance of the VIII cranial nerve. This mismatch is due the typical presence of auditory neuropathy where the peripheral hearing system is spared and the central system is affected. The results of TEOAE are contraindicating with the results of PTA as there should be no OAE present at such higher degree of hearing loss. Bilateral presence of TEOAE in both the cases indicated normal outer hair cell functioning. Transient Evoked Oto Acoustic Emission (TEOAE) testing was done to know the functioning and status of the outer hair cells present in the inner ear.

Poor speech identification scores in both ears for case 1 and case 2 indicated reduced ability of speech understanding and further indication a retro cochlear pathology. Speech audiometry was done to know the speech understanding and perception abilities. Results of PTA indicated bilateral moderate sensorineural hearing loss and bilateral profound hearing loss in Case 1 and Case 2 respectively. Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA) was carried out to detect the behavioral thresholds and to derive the degree and type of hearing loss. Bilateral absence of Acoustic Reflex Threshold (ART) in both the clients indicated abnormal auditory pathway. Results obtained were bilateral ‘A’ type tympanogram in both ears for both the cases indicating normal middle ear. Immitance evaluation was done to see for presence of middle ear pathology. Otoscopy was carried out to rule out any presence of middle ear pathology and the ear canal was found to be clear with the tympanic membrane visible in both cases. Both reported to be having difficulty in understanding speech over telephone and in presence of background noise. No history of trauma, or any other medical conditions. Detailed history was taken and it was found that both were related as father and daughter and both had similar complaints and problems in hearing. Case presentationĪ Case aged 60 years male and another 31 years old Female came to the department with the complaint of reduced hearing sensitivity in both the ears. Recently, authors, suggested that any pathological mechanism that impairs temporal encoding and neural synchrony might be responsible for auditory neuropathy. The lesion could be anywhere from the inner hair cells in the cochlea up to the auditory cortex. Research suggests that auditory neuropathy is due to an abnormality or lesion at the level of the inner hair cells, the synapse between the inner hair cells and auditory nerve, or at the auditory nerve itself. The audiometric results in patients with auditory neuropathy can vary greatly anywhere from normal hearing to severe hearing loss. Patients with normal pure-tone audiograms and absent Auditory Brainstem Responses (ABR) who reported to have difficulty in understanding speech especially in the presence of background noise were reported. Patients with the characteristics of auditory neuropathy were initially reported as early as the 1970’s. However auditory nerve function is disrupted. Auditory neuropathy is characterized by normal outer hair cell function within the cochlea.
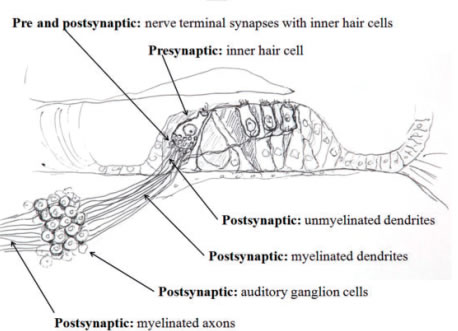
Auditory neuropathy is a disorder where the transmission of the auditory signals from the inner ear to the auditory nerve and auditory brainstem is distorted.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
